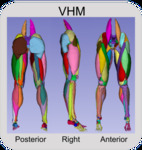
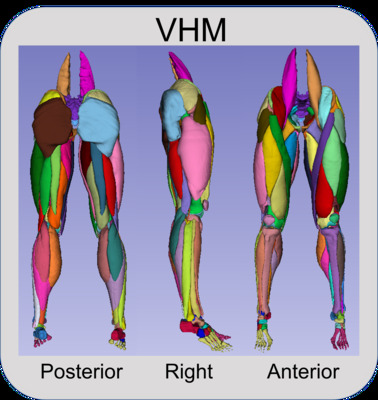
Visible Human Male
Preview
Files
Download Aligned Cryosection DICOM (578.9 MB)
Download Aligned CT DICOM (278.3 MB)
Download Aligned Scan Images (.mat, .tif) (1988.8 MB)
Download Original Segmentation Masks and Aligned Scans (.mhd) (1527.0 MB)
Download Original Segmentation Label Maps (.mat, .tif) (3883.2 MB)
Download Original Segmentation Masks and Aligned Scans (3D Slicer) (3260.3 MB)
Download Smoothed Segmentation Masks and Aligned Scans (3D Slicer) (2773.0 MB)
Download Final Segmentation Masks and Aligned Scans (3D Slicer) (2772.9 MB)
Download Original 3D STL Models (1296.5 MB)
Download Smoothed 3D STL Models (244.0 MB)
Download Final 3D STL Models (133.1 MB)
Download Metadata (57 KB)
Creation Date
2022
Description
Objects Available for Download
- Aligned Cryosection Images: moving proximal to distal in the Visible Human sequences of cryosection images, there are some offsets in the transverse plane that require correction before beginning segmentation. The Visible Human Female images contain some challenging offsets. As correction is a time-consuming process, we have made the corrected images available for download. The corrected scans are available in DICOM, TIFF, .mat, and MHD file formats.
- Aligned and Rescaled CT Images: the Visible Human CT images are useful for segmentation of tissues that are not as clear in the cryosection images. However, the CT images are not precisely aligned with the cryosection images. We have made available the CT images aligned to the cryosection images also with offsets corrected. CT scans are full scans going from the head-to-toes. The corrected scans are available in DICOM, TIFF, and MHD file formats.
- Original Segmentation Masks: the 3D models were created using ScanIP by the construction of 3D objects from a series of outlines, or masks, of each object. This was a manual process often requiring subjective decisions when the clarity of the images made the detection of tissue borders challenging. Therefore, we have provided the segmentation masks in 3D Slicer for those that wish to check or alter the masks for creation of unique models. The raw segmentation masks are available in 3D Slicer as NRRD files. Additionally, the segmentations are available as binary label maps in MHD, TIFF, and .mat file formats.
- Raw 3D Models: the raw 3D models created from ScanIP are provided in STL format in the default edge length of ScanIP, approximately 0.33 mm edge lengths. Providing the raw STL models enables others to apply their own preferred means of post-processing of the objects (e.g., smoothing or lofting) starting from their original state.
- Smoothed 3D Models: the smoothed and resampled STLs from MeshMixer are provided. These geometries are free of issues resulting from segmentation and each geometry was remeshed to the following target edge lengths: muscle 1.5 mm, bone 1.0 mm, cartilage 0.75 mm, ligament 0.75 mm.
- Segmentation Masks of Smoothed Models: segmentation masks were created from the smoothed and resampled 3D models to enable transverse inspection of the final product in segmentation software 3D Slicer.
- Final 3D Models: the goal of the project was to provide 3D models of the tissues that could be used in applications without further processing. The final 3D models were visually inspected to ensure no existing sharp edges and then checked and corrected for any overlap or overclosure. If an overclosure was present, it was removed to provide a gap distance of 0.05 mm using a unique radial basis function-based MATLAB code that is publicly available at: https://github.com/thor-andreassen/femors and described in Andreassen et al. (in review) 2022.
- Segmentation Masks of Final Models: segmentation masks were created from the final 3D models to enable transverse inspection of the final product in segmentation software 3D Slicer.
- Comparison Metadata: includes tables of the initial overclosure amounts tissue geometries as well as comparisons between tissue volumes before and after smoothing and overclosure correction. Comparisons are also made between tissue volumes on the left and right side of the body.
Folders for Download
The complete dataset is very large. For this reason, the datasets have been split into manageable folders for download:
- Aligned Cryosection DICOM
Zip size: 607.0 MB
Extracted size: 578.9 MB - Aligned CT DICOM
Zip size: 291.0 MB
Extracted size: 278.4 MB - Aligned Scan Images (.mat, .tif, .ctbl)
Zip size: 1988.8 MB
Extracted size: 1950.0 MB - Original segmentation masks and Aligned scans (.mhd) (Right, Left, or Combined)
Zip size: 1527.0 MB
Extracted size: 191,000.0 MB - Original segmentation label maps (.mat, .tif)
Zip size: 3883.2 MB
Extracted size: 4070.0 MB - Original segmentation masks and Aligned scans (3D Slicer) (Right, Left, or Combined, Combined with CT)
Zip size: 3260.3 MB
Extracted size: 3410.0 MB - Smoothed Segmentation masks and Aligned Scans (3D Slicer) (Right, Left, or Combined)
Zip size: 2773.1 MB
Extracted size: 2910.0 MB - Final Segmentation masks and Aligned Scans (3D Slicer) (Right, Left, or Combined)
Zip size: 2773.0 MB
Extracted size: 2910.0 MB - Original 3D STL models (Right, Left, or Combined)
Zip size: 1296.5 MB
Extracted size: 8380.0 MB - Smoothed 3D STL models (Right or Left)
Zip size: 244.0 MB
Extracted size: 793.0 MB - Final 3D STL models (Right or Left)
Zip size: 139.0 MB
Extracted size: 238.0 MB - Metadata
Organizational Units
Daniel Felix Ritchie School of Engineering and Computer Science, Center for Orthopaedic Biomechanics
Copyright Statement / License for Reuse

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Document Type
Data Set
Publication Statement
License
Creative Commons License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Liability Agreement
The Data is provided “as is” with no express or implied warranty or guarantee. The University of Denver and the Center for Orthopaedic Biomechanics do not accept any liability or provide any guarantee in connection with uses of the Data, including but not limited to, fitness for a particular purpose and noninfringement. The University of Denver and the Center for Orthopaedic Biomechanics are not liable for direct or indirect losses or damage, of any kind, which may arise through the use of this data.
Citations
T. E. Andreassen, D. R. Hume, L. D. Hamilton, K. E. Walker, S. E. Higinbotham, and K. B. Shelburne, “Three Dimensional Lower Extremity Musculoskeletal Geometry of the Visible Human Female and Male,” Sci. Data, vol. 10, no. 1, p. 34, Jan. 2023, doi: 10.1038/s41597-022-01905-2.
T. E. Andreassen, D. R. Hume, L. D. Hamilton, S. E. Higinbotham, and K. B. Shelburne, “An Automated Process for 2D and 3D Finite Element Overclosure and Gap Adjustment using Radial Basis Function Networks,” arXiv Comput. Sci., Sep. 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2209.06948
Contributing New and Updated Geometries
Adding new geometries is encouraged and can be added to the dataset by contacting the authors. The authors will check new or revised content for accuracy and completeness and update the folders with credit of the contributors highlighted on this website.
Data Records
In total 260 geometries from the Visible Human Male and Female were extracted. The skeletal components consist of the pelvis through the feet (Table 1); the ligament and cartilage components consist of hip, knee, and ankle cartilages and knee ligaments (Table 2); muscle components consist of 76 separate muscles from the Iliacus proximally to the Flexor Digitorum distally (Table 3), and two fat components consisting of the intramuscular fat and fascia, and the outer fat, dermis, and epidermis (Table 4).
Table 1: The 15 skeletal components available for download in both the female and male subjects. Lower limb bones are unique on the right and left sides of the subjects (resulting in 28 unique bones per subject).
- Coccyx
- Sacrum
- Pelvis (Ischium + Illium + Pubis) x 2
- Femur x 2
- Patella x 2
- Tibia x 2
- Fibula x 2
- Talus x 2
- Calcaneus x 2
- Navicular x 2
- Cuboid x 2
- Lateral Cuneiform x 2
- Medial Cuneiform x 2
- Intermediate Cuneiform x 2
- Phalanges (Tarsals + Metatarsals + Phalanges) x 2
Table 2: The 12 identified ligaments and cartilage components available for download in both the female and male subjects. Ligaments and cartilage are unique on the right and left sides of the subjects (resulting in 24 unique tissues per subject).
Knee Ligaments
- Anterior Cruciate x 2
- Posterior Cruciate x 2
- Medial Collateral x 2
- Lateral Collateral x 2
Articular Cartilages
- Femoroacetabular (Femoral Head + Pelvis Acetabulum) x 2
- Tibiofemoral (Distal Femur + Lateral Tibia + Medial Tibia) x 2
- Patellofemoral (Distal Femur + Patellar) x 2
- Tibiotalar (Distal Tibia + Proximal Talus) x 2
Table 3: The 38 identified muscle components available for download in both the female and male subjects. Muscle components are unique on the right and left sides of the subjects (resulting in 76 unique muscle geometries per subject).
- Adductor Brevis x 2
- Adductor Longus x 2
- Adductor Magnus x 2
- Biceps Femoris Long x 2
- Biceps Femoris Short x 2
- Extensor Digitorum Longus x 2
- Extensor Hallucis Longus x 2
- Flexor Digitorum Longus x 2
- Flexor Hallucis Longus x 2
- Gastrocnemius Lateral x 2
- Gastrocnemius Medial x 2
- Gluteus Maximus x 2
- Gluteus Medius x 2
- Gluteus Minimus x 2
- Gracilis x 2
- lliacus x 2
- lnferior Gemellus x 2
- Obturator Externus x 2
- Obturator lnternus x 2
- Pectineus x 2
- Peroneus Longus x 2
- Piriformis x 2
- Plantaris x 2
- Popliteus x 2
- Psoas Major x 2
- Quadratus Femoris x 2
- Rectus Femoris x 2
- Sartorius x 2
- Semimembranosus x 2
- Semitendonosus x 2
- Soleus x 2
- Superior Gemellus x 2
- Tensor Fasciae Latae x 2
- Tibialis Anterior x 2
- Tibialis Posterior x 2
- Vastus lntermedius x 2
- Vastus Lateralis x 2
- Vastus Medialis x 2
Table 4: The 2 identified fat components available for download in both the female and male subjects. Fat components are unique on the right and left sides of the subjects but contained in single files (resulting in 2 unique fat geometries per subject).
- Intermuscular fat and fasciae
- Outer fat (epidermis + dermis + fat)

